How Blockchain Technology Works and Types of Blockchain Explained
\”The modern era is all about technology. People from all over the world expect modernization in their everyday lives and they welcome any new technology with open arms. Technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Augmented Reality, IoT have gained a lot of attention in the past decade and now there is one more addition to the squad – The Blockchain Technology.\”
What is a Blockchain?
In simple terms, blockchain is a system to capture information securely, therefore, making it impossible to modify, delete, or hack the information. Blockchain technology falls under the category of distributed ledger technology, and yes, it is a digital ledger of transactions distributed across millions of computers.
Multiple blocks together contribute to a blockchain. Each block in the chain holds a certain number of transactions, and whenever a new transaction occurs on the blockchain, a time-stamped record of the new transaction is included in the ledger. This decentralized database is managed by multiple participants, hence the name Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT).
Call/Whatsapp : +91 8946015133 | Telegram : @blockchainfirm | Email: info@blockchainfirm.io
How to create a blockchain?
A tech-savvy person can write their own code to develop a new blockchain supporting native cryptocurrency. However, you will need extensive technical knowledge and practical training to code a blockchain. Still, there is a chance of blunders in the outcome.
This is what your roadmap for developing a blockchain will look like.
Step 1: Identify a pain point to rectify
Step 2: Determine your business needs
Step 3: Choose the suitable consensus mechanism
Step 4: Choose a preferred blockchain platform
Step 5: Design your blockchain nodes
Step 6: Determine your blockchain configurations
Step 7: Start building your APIs
Step 8: Design the user interface
On the other side, there is another way to create a blockchain. Consult with an industry expert to avail the best Custom blockchain development service. At Blockchain Firm, we will help you build an avant-garde blockchain with the required customizations for your business.
Here are the properties of the Distributed Ledger Technology:
- 1. Secure
- 2. Anonymous
- 3. Unanimous
- 4. Distributed
- 5. Immutable
- 6. Programmable
- 7. Time-Stamped
What’s so Special About a Blockchain?
In a blockchain network, transaction blocks are secured with an immutable cryptographic signature, and that’s known as ‘hash.’ This immutability feature is the guardian angel of every blockchain, because if one block is modified or deleted, then it would reflect in all the previous and current blocks. If hackers want to hack the network, they will have to change every single block in the distributed network, which is ‘impossible.’
“Bitcoin and Ethereum Blockchains are continually growing as new blocks are being added to them very often, which in turn enhances security.”
Before the introduction of blockchain, there were several attempts to create digital currencies. But all those resulted in failure because of one single issue – ‘trust.’ Bitcoin was created to solve this issue with the aid of a secure database, and that’s blockchain.
Usually, regular databases are controlled either by an entity or an individual, whereas blockchain is not the same. Nobody is in charge of a blockchain network; instead it is run by its participants. No one can fake or duplicate bitcoins or any other cryptocurrencies since this dynamic technology backs them. Besides, people owning bitcoin have a reason to believe that it has a value.
How much does blockchain application development cost?
Like you might have guessed earlier, there are no standard ways to determine the blockchain application development cost. It varies from one project to another. In most cases, the price will range averagely between $90,000 and $500,000. Certain factors that impact the overall blockchain app development cost are UI/UX design, app features, the complexity of the application, team strength, and PoC.
The blockchain is a more straightforward way of transferring data from one person to another in a secure and automated manner. An individual wanting to do a transaction, initiates the process by creating a block and this block is checked by thousands and millions of participating computers distributed across the network. After being verified, the block with a unique identity is added to the chain.
Outstanding Features of Blockchain Technology
1. Immutability : A Blockchain Network is Incorruptible
Immutability is the ultimate feature of this dynamic technology. Being immutable means showing resistance to alterations or changes. A blockchain network is a permanent one, meaning no one can delete it and it is also unalterable.
Blockchain, instead of depending on centralized databases, operates through a collection of nodes. Each node shares a copy of the digital ledger. Whenever a new transaction needs to be added, all the nodes should check the validity, and the majority decides the result. This method enhances transparency to a greater extent and also makes a network hack-proof and corruption-free.
It is clear that without the consent from the majority of participants, no new transaction blocks can be added to the chain. The participants can only view the transaction,and they cannot edit, update, or delete it.
2. Decentralized Network
A blockchain network is a decentralized one. It means that there are no governing authorities or individuals to look after the framework. Instead, a set of nodes regulates the network, thus making it decentralized.
This feature is the one that led blockchain to soar heights. To be more simple, blockchain makes the participants transact in a direct manner. Since there are no entities to control the network, a user can simply access it from anywhere and store his/her digital assets there.
The users can store anything in a blockchain, For example, digital currencies, personal or official documents, agreements, and other important assets. And with the help of a unique private key, the users have complete and direct control over their information. Besides, users do not have to rely on any third parties to organize their assets.
A blockchain network is safe from malicious and ransomware attacks. Since hackers cannot intrude into the system, it is less prone to breakdown. The decentralized nature makes blockchain a system free from third parties. No involvement of third parties, no additional fees or risks; it’s that simple.
3. Ultimate Security
Since there is no dependence on a central authority, no parties can change data in a blockchain network. Along with that, encryption provides an additional layer of security for the network.
You may ask, How is blockchain this much secure? The answer to that question is ‘with the aid of cryptography.’ In addition to decentralization, cryptography ensures another layer of protection for the network and as well as the users. To be technical, cryptography principles are a set of mathematical algorithms acting as a defender against malicious attacks.
Each block in the blockchain is time-stamped and hashed cryptographically. The information in the network is hidden from its true form. The hashes are different from one another and no two blocks can have the same identity. And so, trying to tamper with the data means changing the hash IDs which is impossible. All users will have a private key to access their data and a public key to initiate transactions.
4. Consensus Mechanism
Every blockchain network survives with the help from consensus algorithms. The architecture of a system powered by this technology is intelligently framed, and consensus algorithms are at the core of this framework since they help in finalizing decisions.
In simpler terms, a consensus is a decision-making process for the participants who are currently active. The participants or nodes decide upon an agreement easily and quickly. When millions of nodes check a transaction, consensus backs the network and makes the process run smooth.
The consensus has another essential role to play, i.e., maintaining the system to be a trustless one. Nodes need not trust each other, but they can rely on the algorithms. This is the primary reason for the majority party to win a decision.
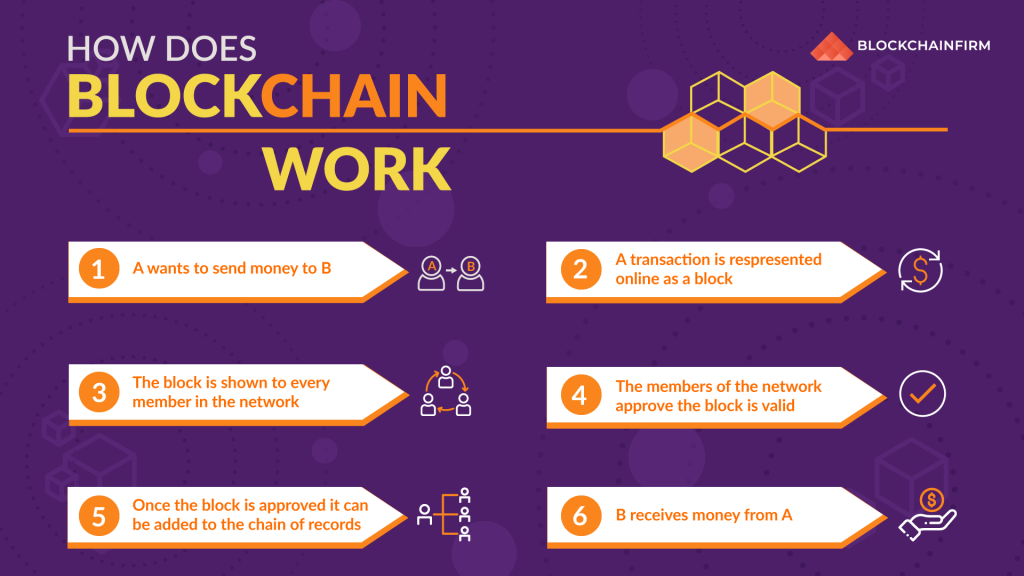
How Does a Blockchain Work?
The Functioning Of Blockchain
To understand the working of blockchain, we should be aware of three components:
- Private Key Cryptography;
- Distributed Network;
- Confirmation Process
1. Private Key Cryptography
Let’s think of two persons participating in a transaction. They will have possession over two keys: public and private keys. By bringing together these two keys, the cryptographic function allows the participants to create a secure digital signature which is one of the vital components of a blockchain. This signature is used to verify, certify, and control ownership.
2. Distributed Network with a Shared Ledger
The digital signature is then merged with the distributed network component. As we all know, blockchain is an extensive network of participants, and they act as validators to check transactions. This process is done by mathematical verification, and it secures the blockchain network. Cryptographic keys coupled with distributed networks, blockchain paves the way for new digital interaction types.
3. Confirmation Process
This is the crucial aspect of blockchain because of the way it checks and certifies transactions. As we have seen above, an individual who wants to send information uses his/her private key to attach the transaction details to the public key of the receiver. These together form a block, and the block comprises a cryptographic signature, a time-stamp, and other data related to the transaction. However, the identities of the persons involved in the process are not revealed. Whenever a block is completed, it is transmitted to the distributed system and added to the chain.
How Transactions Take Place in a Blockchain Network?
- When a transaction is initiated, the network makes use of private & public keys to generate a digital signature, therefore, making sure security & consent are satisfied.
- Within a fraction of seconds, the authenticity of the transaction is verified through these keys. And after that, the need for authorization from the participants arises.
- Blockchain makes it feasible for the network participants to conduct mathematical operations to verify the transaction and reach a consensus to agree on one defined value.
- While initiating a transfer, the sender makes use of his unique private key to inform the transaction initiation over the blockchain network.
- A transaction block is then created that comprises information such as a timestamp (time of creation), digital signature, and the receiver’s public key as well.
- The system automatically announces the information about this block over the network. And then the validation process commences.
- To process the transaction, miners from all over the network begin to solve the mathematical equation related to it. This process requires miners to invest their significant computing resources.
- Whoever solves the equation first, he/she receives bitcoins as a token of appreciation. These kinds of problems are usually referred to as PoW (Proof-of-Work) mathematical problems.
- When a majority of the participating nodes in the blockchain network come to a conclusion and agree on a valid solution, a consensus is created.
- The verified block is then time-stamped and added to the existing chain of blocks. These blocks usually contain money or important messages.
- Once the newly created block is added to the chain, the existing blockchain copies are updated across all the nodes on the network.
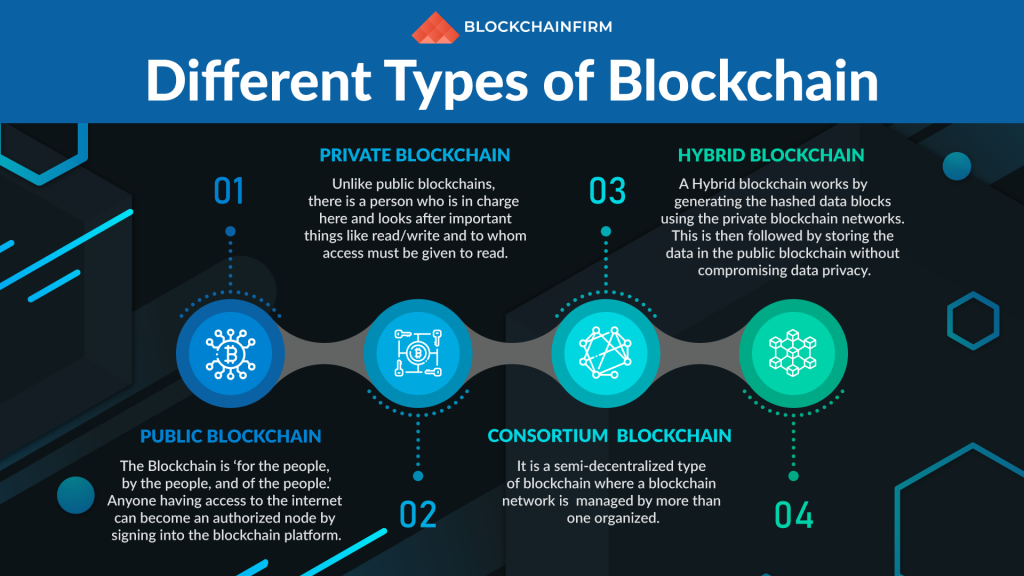
Types of Blockchain:
- 1. Public Blockchain / Permissionless Blockchain
- 2. Private Blockchain / Permissioned Blockchain
- 3. Federated Blockchain / Consortium Blockchain
- 4. Hybrid Blockchain
Practically, blockchain could be implemented in four different ways. We are going to dig deeper into each one of them.
1. Public Blockchain / Permissionless Blockchain
Public blockchains are also called permissionless ledgers/blockchains. As the name indicates, everyone can access this type of blockchain. The user just needs Internet access to download and use a public network. Besides, the users can take a look at the overall history of the blockchain and also initiate transfers.
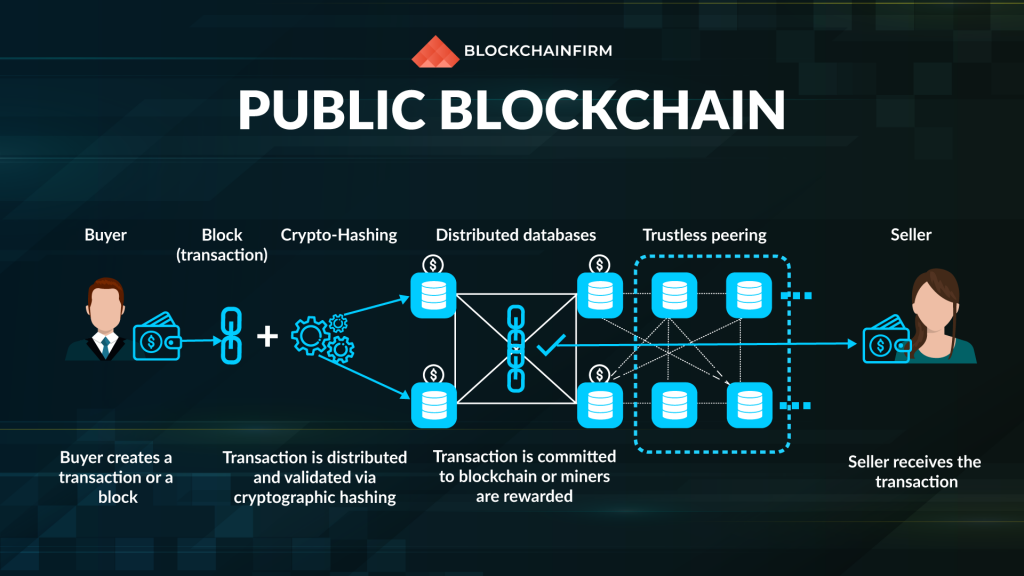
Public Blockchain networks reward their participants for taking part in the mining process and regulating the flow of the transactions while simultaneously maintaining the immutability of the ledger. A simple and popular example of a public blockchain is the well-known Bitcoin Blockchain.
This kind of permissionless blockchains allows the communities across the globe to trade information publicly and securely. The only disadvantage is that these blockchains can be modified under favourable conditions if the rules are not implemented properly. Other than that, public blockchain networks have gained pace in recent years.
2. Private Blockchain / Permissioned Blockchain
They are the total opposite of public blockchains. Private blockchain networks are shared only among the trusted participants. The control of a private network lies in the hands of the owner. However, the owner cannot be involved in any suspicious activity since the ledger is immutable. The rules that a private blockchain abides by can be customized depending on levels of permissions, exposure, number of participants, authorization requirements, and a lot more.
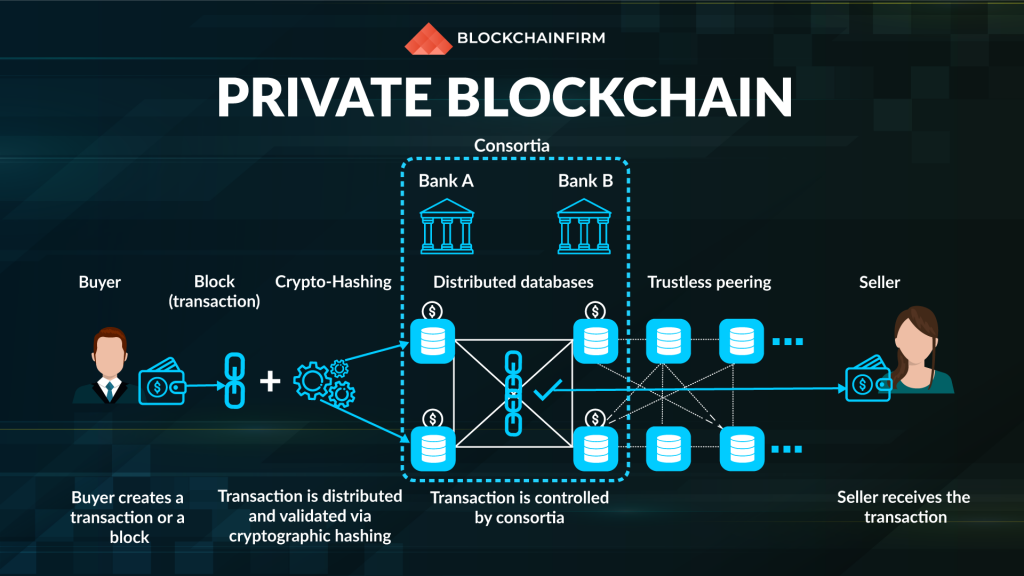
They are also known as permissioned ledgers, and they are programmed to operate without depending on any source. Yet, they can be incorporated with other blockchain networks, and corporate companies and enterprises generally employ this method. Thus, it is evident that the level of trust among the participants is undoubtedly higher in private blockchains.
In a private network, the existing parties limit the access of the blockchain. New users who want to be a part of the network need to request access from the authority who is in charge of managing the blockchain. One more thing to notice here is that a private blockchain is not entirely closed to the public. It depends on the administrator whether the access is kept public or private.
Federated Blockchain / Consortium Blockchain
Consortium blockchains are partially decentralized blockchain networks. The network here is managed by two or more entities. These blockchain networks work on an entirely different consensus process. Pre-selected groups of nodes regulate them.
This federated blockchain resembles a hybrid blockchain because it is shared among multiple participants, and the restriction is levied on nodes from accessing the network. This type of blockchain is useful when a group of enterprises wish to share a blockchain but restrict access only to themselves.
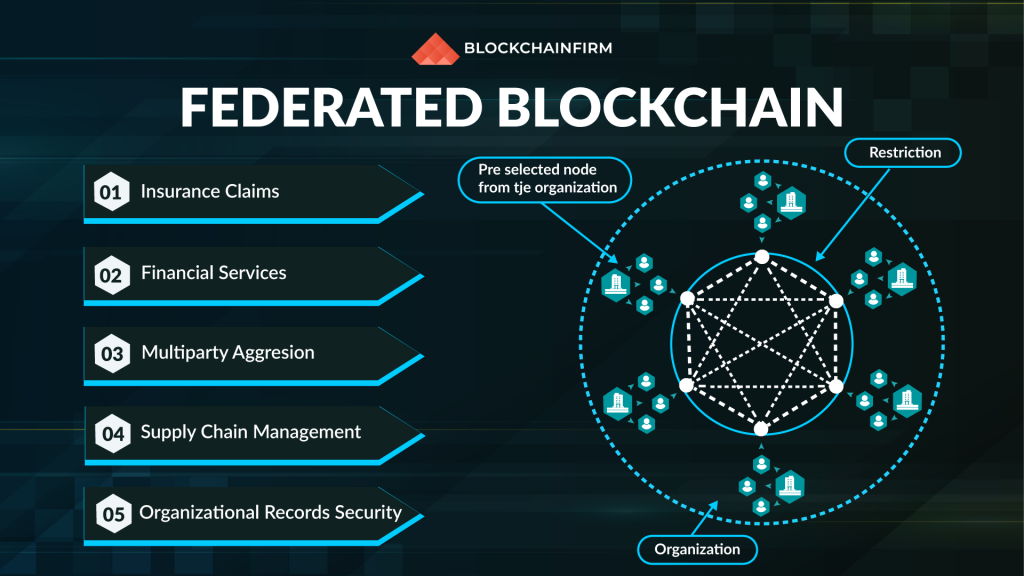
There are two categories of users in a consortium blockchain: the first category is the users who possess control over the network and decide who should have access permission. The second category is the users who can just access the blockchain.
When the question ‘Who will control the blockchain?” arises, we will be surprised to find many individuals put in charge. They are the representatives from each organization in the network, and together they make decisions that benefit the network on the whole.
The federated blockchain helps in reducing the transaction costs and redundancy of data while being faster and offering higher scalability.
Hybrid Blockchain: A Duo of Public and Private Blockchains
A Hybrid blockchain is defined as the one that uses both permissionless and permissioned blockchain solutions. To be precise, a hybrid blockchain offers controlled access and complete freedom, both at the same time. A hybrid blockchain network is not open to all. However, it includes features such as transparency, integrity, and security.
Hybrid blockchains are totally customizable. The existing members of this blockchain decide who can participate in the network and who cannot and also which transactions are made public and which are kept private. This type of blockchain opens up the door to the best possible way that an organization can work with its shareholders.
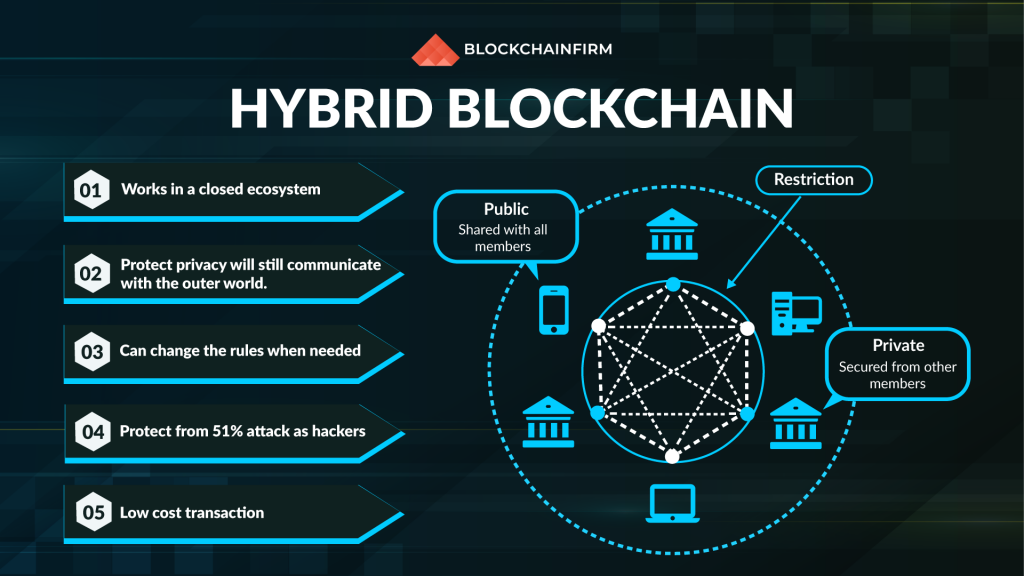
Though the transactions are not public in a hybrid blockchain, they can be verified whenever the need arises. The transactions once completed, are kept private, and they are opened when the participants need to check. The immutable nature of blockchain technology ensures that the transactions are permanent, and there is no way to alter or delete them.
Once a user is provided access to a hybrid blockchain network, he/she can participate wholly in the activities of the blockchain. Each participant has equal rights to initiate transactions and to view the completed ones. However, to protect their privacy, the identity of users is still kept a secret from the eyes of the participants.
About Blockchain Firm
Blockchain Firm is a standardized company offering enterprise blockchain development services. We are a team blended with intelligent minds and smart problem solvers. We help you incorporate blockchain technology with your business and identify business outcomes, prioritize use cases, and develop a minimum viable product.
Our services are not limited to blockchain development. We do offer DApps Development, Smart Contracts Development & Audit, Android & iOS Mobile App Development, and Cryptocurrency-based Products.
