“The Decentralized Future is nearing. As more number of blockchain-based DApps emerge, a wider picture will open up the door for us to witness how smart and transparent our world could become. ”
What are DApps or Decentralized Applications?
DApps are not a closed circle to be explained in a single line. They are a new category of open source applications powered by blockchain. No one controls DApps, and one can neither shut them down nor manipulate the data. Since they are backed by blockchain, no intermediaries are required to regulate the data flow.
“To be more accurate, Blockchain is to DApps like the Internet is to Email.”
Decentralization is an emerging and progressive concept that is entirely private, free, and not governed by any central authority. Applications developed using decentralization lay complete control on the hands of the users.
Traditional Apps Vs. DApps
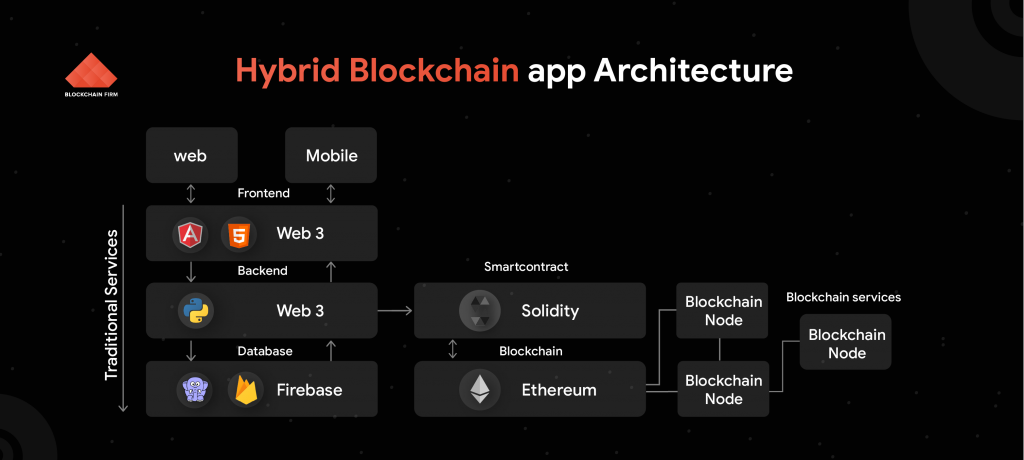
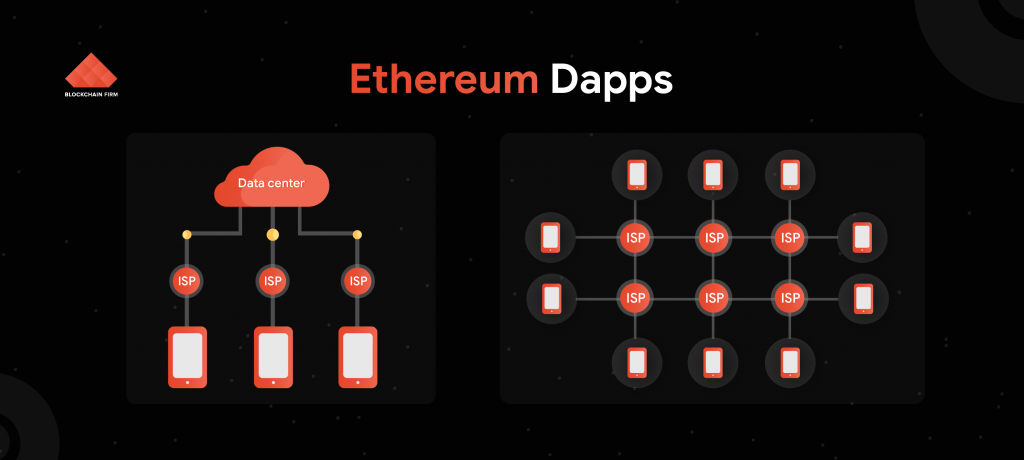
Both traditional applications and DApps utilize two crucial factors: the front-end and the back-end. Traditional web apps make use of HTTP protocol to establish communication between the elements, whereas DApps are developed with a few exceptions.
Traditional Apps
A centralized network hosts all the application servers, meaning that there is a single point of failure. In the case of malicious attacks or data breach, the entire centralized system is at risk.
Hackers can easily intrigue to interfere with the hosting service. They can manipulate the data or install ransomware and go unnoticed because of the weak security standards of the centralized network.
Blockchain-backed DApps
The back-end of DApps is a blockchain network comprising a distributed network of systems. Immutability is the primary feature of the blockchain network, and so the data stays secure inside the network.
It is nearly impossible for hackers to enter into a blockchain network and manipulate the data. To do that, a hacker has to modify all the distributing nodes since they are cryptographically secure.
Eligibility Criteria to Enter the Realm of DApps
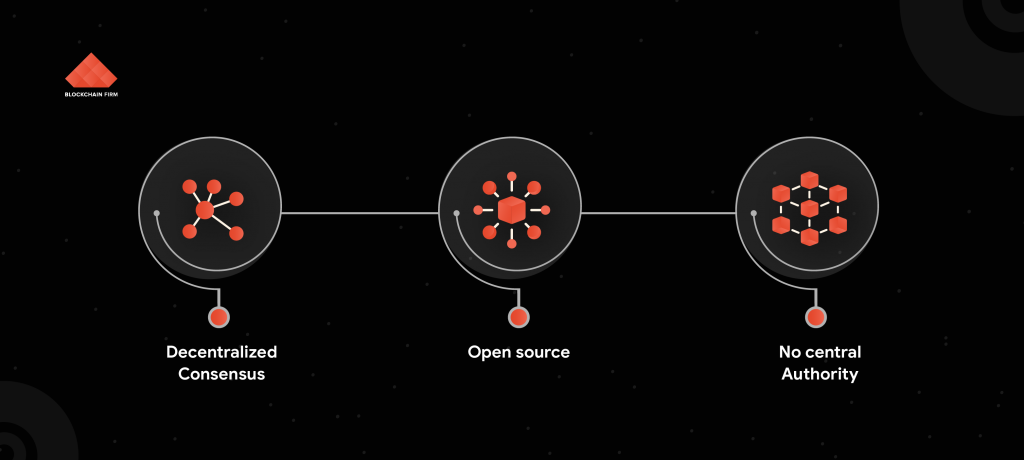
Open Source
- DApps do not rely on any authorities to govern them. They operate autonomously. The source code of a Decentralized Application is always open to the participants from all networks.
- Developers can copy or share the code with others for free without any restrictions. All participants in the network can keep track of the events occurring & contribute their part in decision making.
Cryptographically Secure
- The dynamic distributed ledger technology (blockchain) is the backbone of DApps. All data and records relating to a particular application are stored on a decentralized public blockchain.
- Since the network is cryptographically secure, there is no central failure point. The code that regulates the back-end runs on a distributed system of computers, hence hack-proof.
Crypto Token-based
- It’s a necessary thing for DApps to be fueled by crypto tokens. Crypto Miners, in return for their contribution to the network, are rewarded with these tokens.
- This type of token incentive system encourages a broad group of participants to stay on the network and maintain the chain balance. These tokens can also be used to access the applications.
Consensus Mechanism
- DApps, powered by blockchain, make use of consensus mechanisms with which they facilitate communications among their users.
- PoW (Proof-of-Work) & PoS (Proof-of-Stake) are the two powerful algorithms that help in setting up a reliable consensus system.
- PoW aids in making changes relating to miners’ contributions, while PoS helps to finalize decisions concerning the percentage of stakes.
How are DApps Categorized?
DApps are categorized into three types depending on their areas of use.
Finance-based DApps
- Blockchain-based applications under this classification provide users with different techniques to manage their financial expenditure.
- In this type of app, no central party regulates the money. People in the network & consensus mechanism are the sole owners of their money.
Semi-Financial DApps
- The decentralized applications that regulate cash flow and information outside the blockchain network fall under this category. E.g., Insurance-based apps.
- ICOs, the fame of 2017, also set an example for this category. It’s easy to develop ICO DApps since they employ standards such as the ERC20 Token Standard.
Full-Functioning DApps
- The DApps under this classification utilize all the features of decentralized and distributed systems. These apps are the most popular ones among the three.
- They are stamped as “non-financial” under all levels. The applications used for digital voting or decentralized governance are a few examples.
Benefits of Decentralized Apps
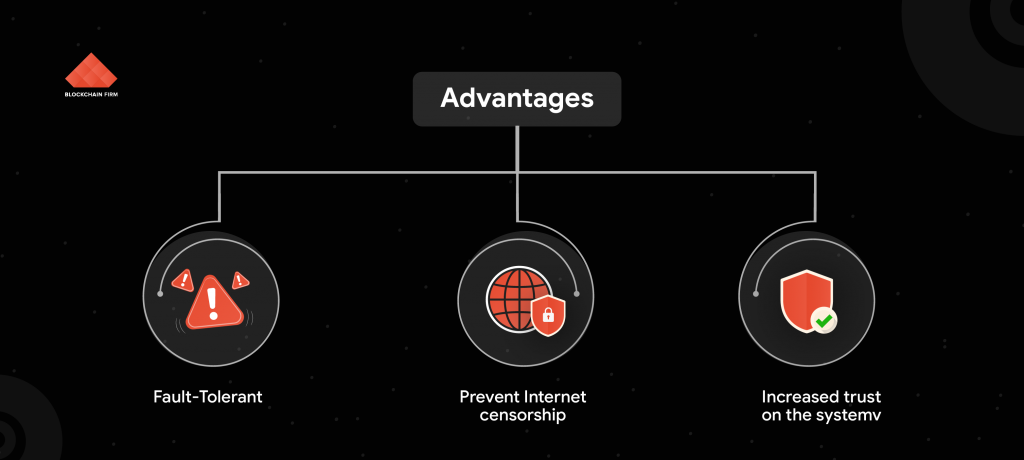
Not Relying on Third Parties
- DApps pave the way for sellers and buyers to interact directly without the involvement of intermediaries.
- With this top-notch benefit, DApps help to cut the cost and time spent on availing services from third parties.
Censorship Independent
- Decentralized Applications are blockchain-powered, which means that they do not have a controlling agent. Therefore, we can trust them completely.
- Since the transactions are open to the public, all the participants can verify the status and history anytime, and this makes DApps more transparent.
No Compromise on Security
- DApps are highly secure; no hacker can manipulate our data or steal it. If a hacker wants to perform data manipulation, he has to modify all the nodes, which is impossible.
- Besides, no system can shut down a DApp, since it does not rely on a centralized server, but a distributed network of computers across multiple nodes at various locations.
No Downtime & 100% Uptime
- The larger the capacity of the blockchain network, the better the pace of the DApp. As the power of the network increases, the performance of the DApp increases simultaneously.
- With data copies on multiple devices, DApps are programmed to have 100% uptime. With an increased set of devices, a DApp becomes more reliable, secure, and more responsive.
- Apps that rely on centralized servers will have frequent downtimes due to power outages and server crashes. In the case of a DApp, there is no single hosting point; therefore, no downtime.
How is DApp Developed?
- Whitepaper Creation – The outline of the DApp is described here.
- Token Sale – The sale of tokens is announced.
- Initial Coin Offering – The ownership is shared among investors.
- Development & Implementation – A feature-packed app is developed
- Launching the App – The app goes live after testing.
Ethereum DApps
Ethereum was the first and foremost blockchain platform for decentralized applications. Ethereum Virtual Machine or EVM was the superficial technology behind the successful running of Ethereum dApps.
“A Turing EVM is a device capable of simulating and executing computer algorithms. A smart contract or a decentralized app code can be programmed for EVM and executed by the decentralized ethereum computer network.”
Ethereum DApps Vs. Smart Contracts
The primary difference between an Ethereum-backed DApp and a Smart Contract is that besides functioning as a Smart Contract, Ethereum dApp involves a front-end application for User Interaction.
The most trending DApps on Ethereum are:
- Games
- Decentralized Exchanges
- Marketplaces and Gambling
Conclusion
Every new technology takes its own time to become popular. It’s the same in the case of DApps. But sooner or later, we can witness DApps becoming the next big thing in the digital world. Blockchain enthusiasts believe that DApps could be the long-awaited change the Internet community is hoping for.
