Blockchain For Supply Chain Management
The supply chain is a huge network and it’s more complex than it was a decade ago. As of now, a payment, after being initiated by the supplier, takes days to reach the manufacturer. On the other hand, contractual agreements between parties need support from lawyers & banking systems. This results in the summing up of additional costs and time delay. Products are sometimes hard to track, leading to difficulties in eliminating item defects.
Whether it is machinery, consumer goods, medicines, food products, or online offerings, supply chains are still cumbersome.
What Are The Issues With The Current Supply Chain?
One major problem in the supply chain is Friction. Too many intermediaries, hefty back & forth processes, and the rise in uncertainty create lags in the supply chain and stops it from functioning well. A centralized organization acts as the intermediary between manufacturers & consumers and providers & clients. Obviously, simpler transactions become more complex, turning into lengthy, multi-step procedures.
Research the hype and facts but understand blockchain is a game changer for supply chain– SupplyChainToday
How Could Blockchain Serve As A Problem Solver?
Blockchain is the ultimate solution to the aforementioned issues. This game-changing technology backs the most popular Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. Despite serving as an unhackable method for holding & transferring currencies, blockchain is capable of managing all kinds of exchange agreements, transactions, and tracking processes as well. Blockchain applications in supply chain correlate to automates smart contracts to cold chain management.
A Supply Chain Blockchain Preliminary
Many people still have the doubt of what is blockchain. Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology. The digital ledger stores transactions in the form of blocks across a network of computers. They are known as nodes. Every new transaction block is connected to the previous block. This makes the ledger secure and thus, tampering is nearly impossible.
The blockchain ledger is a decentralized framework, hence no need to depend on a centralized organization for storing the records. Whenever a new transaction occurs, the existing nodes associated with the blockchain network receive the latest versions of the ledger.
Blockchain Beyond Bitcoin & Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are backed by blockchain; bitcoin is a real-life example of this budding technology. Digital currencies can be brought from crypto exchanges and the currencies can be used to make & receive payments.
Whenever a payment is made, the respective transaction is recorded in the ledger. Any user with access can verify the amount, time, & date of the transactions at any time. Bitcoin holders literally do not know to whom they are paying or receiving. Bitcoin employs another distributed system known as mining to include transaction blocks in a secure & tamper-proof way.
What is Blockchain in Supply chain? An Onset
Consensus Mechanism
All the entities in a blockchain network go on the same terms and agree that each transaction is valid. For cryptocurrencies, that denotes the transfer of cryptos and for supply chain, it refers to payment, warehousing, shipping, and delivery.
Provenance
Each entity in the network knows how & where each asset originates from. They can also find the previous owner’s details. The assets can be any, from digital assets to raw materials to wheat or corn, cash, machines, and copyrights.
Immutability
It is impossible to enter and tamper the data in the distributed ledger. Only a crypto transaction can have an impact on another transaction and also no supply chain transaction or the inventory records or delivery times & dates.
Beyond Cryptocurrency To Business Blockchain
Bitcoin is one way to explain the blockchain technology and blockchain supply chain management also adheres to the same principles. But, the techniques differ in a hefty way. Blockchain for business and in particular, for the supply chain is not committed to utilizing the mining concept. There are also additional options to update a business blockchain securely.
Blockchain applications in the supply chain are far more distinctive than making or receiving payments. A huge part of this diversity nature comes from the application of smart contracts.
Blockchain is a Key Technology in the Digital Supply Chain– EverythingSupplyChain
What Are Smart Contracts By The Way?

A smart contract is a dynamic self-executing software program that uses blockchain to process an agreement. The program is stored on the distributed ledger technology so that they can function according to the designed programming. There are no possible ways for fraud or other interferences.
A smart contract takes the input from a ledger and then triggers an event. For example, in the supply chain, the smart contract initiates delivery after receipt of payment as part of a transaction. Contrarily, if a need, for example, timed delivery or proper storage, is not satisfied, the smart contract can also initiate a penalty or similar sanction.
Third-party involvements are not essential for the execution of smart contracts. Human checking of conditions and events are complete endeavors. A software program that is automated using information that is approved by the blockchain saves both time and money.
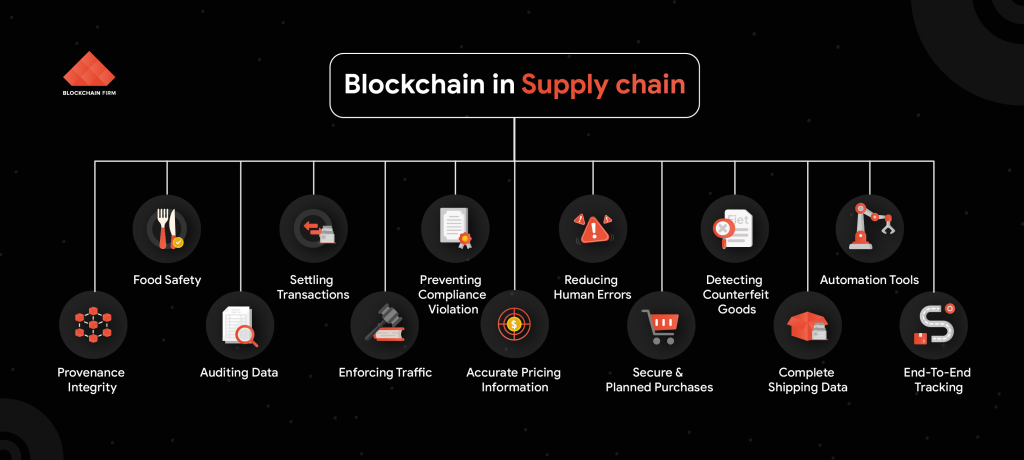
Blockchain Applications in Supply Chain
Payments In The Automotive Sector
Blockchain paves an efficient way for fund transfer across the globe without integrating conventional banking transactions. In the blockchain, transactions are peer-to-peer, i.e., payments made by the payer reach the payee directly. The transactions are one-hundred percent secure and rapid. When compared, cryptocurrency transactions incur lower charges than other payments.
Meat Traceability
Food & meat-based companies can employ this distributed ledger technology to record the status of a product at each stage of production. The records stored are permanent, immutable and they provide a way to trace each product to its source.
Electricity-Powered Micro-grids
Almost all kinds of entities can utilize blockchain technology, no matter the size of the organization. To be accurate, blockchain is not limited to the big players only. With smart contracts, companies can categorize and redistribute excess power from solar panels.
RFID-governed Tenders and Execution
RFID tags are used in the logistics to store information about products. The desired sensors or systems can read the tags and then process them automatically. RFID tags for pallets or cartons store delivery location data, date & time. Shipping partners run applications to check the tags and put forth a bid for assigning delivery contracts. The delivery partner who offers optimal price and service gets the deal. A smart contract then tracks the status and final delivery performance.
Cold Chain Monitoring
Food and pharmaceutical products often have specialized storage requirements. Enterprises find it beneficial in shared spaces, warehouses, and distribution centers. Sensors are embedded in sensitive products. They can record temperature, pressure, humidity, and other climatic conditions. The values are then stored on a blockchain. If a situation arises where a storage condition deviates from what is set, every member of the blockchain will get notified regarding the same.

Conclusion
Blockchain is capable of transforming supply chain industries, and ecosystems. Even organizations like banks can look for opportunities to exploit the tech in streamlining their operations. An in-depth transformation is impossible to happen in a day. However, supply chains can start adopting blockchain in some operations. Smart contracts on the other hand, can help eliminate costly delays and waste generated by manual handling.